

Many professions require these mathematical skills, often used in conjunction with much more complex geometry and trigonometry. In the case of circular shapes, it is called a circumference. Perimeter is the mathematical term used to define the total length of the edges of a multisided two-dimensional enclosed shape (polygon). Whether you want to brush up on your basics, or help your children with their learning, this is the book for you. These concepts are built up through the book, with worked examples and opportunities for you to practise your new skills. This eBook covers the basics of geometry and looks at the properties of shapes, lines and solids. Part of The Skills You Need Guide to Numeracy However, if you just need to replace your garden fence, you will probably be fine with just a tape measure and a ball of string! These are used in conjunction with other instruments such as levels and theodolites, which ensure the accuracy and precision of angular measurements, using a mathematical technique called triangulation. Electronic distance measurement (EDM) devices, which use electromagnetic waves, are more often used by land surveyors. Relatively short distances can be measured using steel tapes, or measuring wheels. It is not only the lengths of the lines that are important, but accurate measurement of the angles between those lines.Īpart from mathematical knowledge, there is also an interesting and varied toolkit needed for these sorts of occupations.
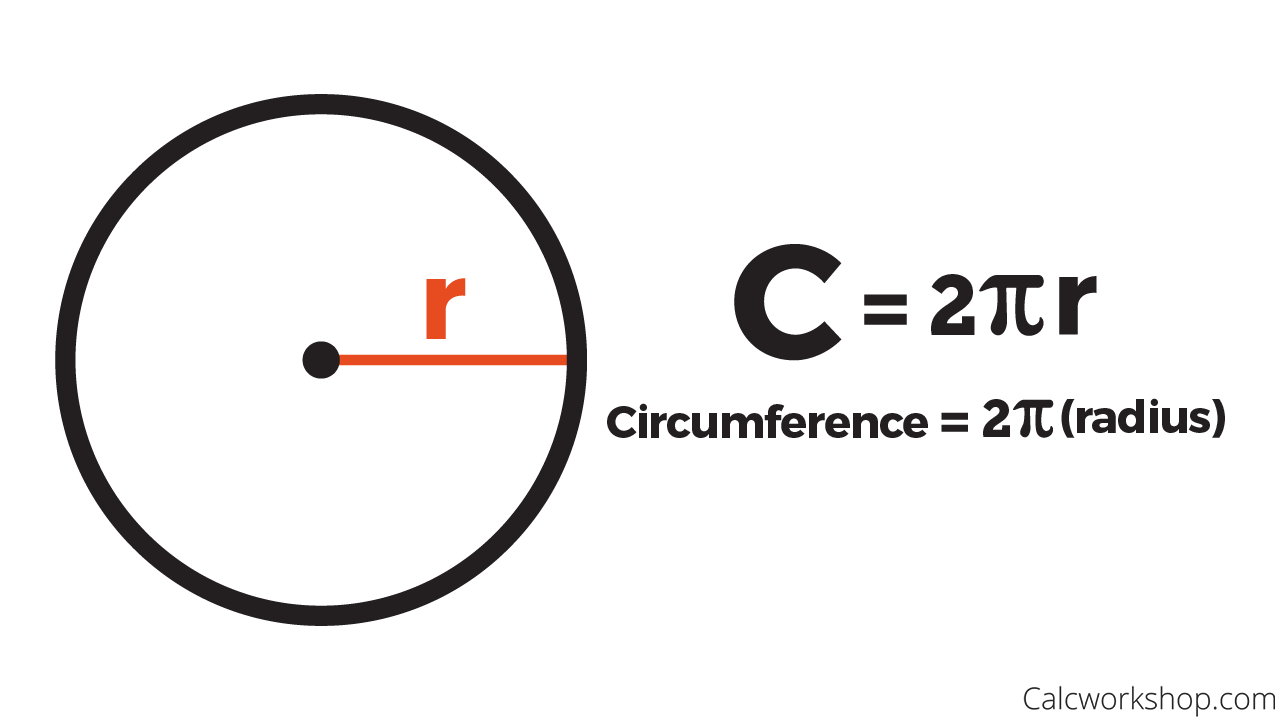
It is necessary to not only have an understanding of the basic mathematical principles above, but also more advanced numeracy tools, such as trigonometry. There are many professions and occupations that may require you to take physical measurements of perimeters and boundaries, such as civil engineering, surveying, landscape architecture, garden design and sports ground maintenance. Exampleįind the perimeter of a rectangular football pitch, measuring 105 × 68 m. Measuring Perimeter of Irregular PolygonsĪ regular polygon has all sides and internal angles equal, irregular polygons do not.Ī rectangle that is not an exact square, for example, has two pairs of sides of equal length, but all four sides are not the same length. So for example, if you have a heptagon (7 sides) with side length 15cm, then the length of the perimeter is 7 × 15 = 105cm.įor more on regular, irregular and other polygons (straight-sided shapes), including a helpful chart with illustrations, see our page on properties of polygons. If your polygon has n number of sides, all of length s, then its perimeter is always equal to n × s, or simply ns. You can use the same principle to work out the perimeter of any regular polygon that has any number of sides of equal length: m 2, cm 2 or inches 2.įor more on measuring area, see our page on Calculating Area. So whilst perimeter is measured in units of length, area is measured in square units, e.g. Whilst perimeter is the measurement of the outline of the shape, area is the measurement of the space contained within the perimeter. The square has four sides of equal length, which are added together.ĭon’t get confused between perimeter and area. The perimeter of a two-dimensional shape is the total length of all the sides added together.įor example, the perimeter of a square, with a side length of 6m, is simply four lots of 6m, i.e. However, in a mathematical context, we only use perimeter.Ī circumference is a very specific type of perimeter, that refers only to circular shapes and forms. So in common language, the two are often used interchangeably. For more on this, see our page on measurement systems. Perimeter is measured in any unit of length, e.g. In geometry, it is defined as the sum of the distance of all the lengths of the sides of an object.

The perimeter is the measured length of such a boundary. In cricket, the boundary is the line marking the edge of the pitch. The definition of a boundary is a dividing line between two areas. Understanding Statistical Distributions.Area, Surface Area and Volume Reference Sheet.Simple Transformations of 2-Dimensional Shapes.Polar, Cylindrical and Spherical Coordinates.Introduction to Cartesian Coordinate Systems.Introduction to Geometry: Points, Lines and Planes.Percentage Change | Increase and Decrease.Mental Arithmetic – Basic Mental Maths Hacks.Ordering Mathematical Operations - BODMAS.Common Mathematical Symbols and Terminology.Special Numbers and Mathematical Concepts.How Good Are Your Numeracy Skills? Numeracy Quiz.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
